Non-woven fabric is a type of material made from fibers that are bonded together using a variety of techniques such as heat, chemical, or mechanical methods. Unlike traditional fabrics that are created by weaving or knitting yarns together, non-woven fabrics are created by layering and bonding fibers together to form a web-like structure.
What is Non-Woven Fabric?
The fibers used in non-woven fabrics can be made from a variety of materials such as synthetic polymers, natural fibers like cotton, or a combination of both. These fibers can be either long or short, and they may be laid down in a random or specific pattern depending on the intended use of the fabric.
Non-woven fabrics are commonly used in a wide range of applications such as medical textiles, filters, geotextiles, automotive textiles, and home furnishings. They are valued for their durability, strength, and versatility, as well as their ability to be produced at a lower cost compared to traditional woven fabrics.

Who Invented Non Woven Polypropylene Plastic?
Non Woven polypropylene plastic was invented by two Italian scientists, Giulio Natta and Karl Ziegler, in the mid-1950s. They discovered the process for creating polypropylene while conducting research into new types of polymers at the Max Planck Institute in Germany.
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer that is commonly used in a wide range of applications such as packaging, textiles, automotive components, and medical devices, among others. Its versatility, durability, and resistance to chemicals and heat have made it a popular material for a variety of industries.
Natta and Ziegler’s discovery of polypropylene was a significant breakthrough in the field of plastics, and it has since become one of the most widely used polymers in the world. For their work on polypropylene, Natta and Ziegler were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1963.
What is Polyester Fabric?
Polyester fabric is a synthetic fabric made from polymer fibers, most commonly from polyethylene terephthalate (PET). The polymer fibers are made by melting down the polyester resin and extruding it through tiny holes to create long, thin fibers that are then spun into threads.
Polyester fabric is known for its durability, wrinkle-resistance, and easy care. It is also lightweight, quick-drying, and has excellent resistance to chemicals and mildew. Additionally, polyester fabrics can be made in a wide range of textures and finishes, from smooth and silky to rough and textured.
Who Invented Polyester Fabric?
However, it was not until the 1950s that polyester fabrics became widely available for commercial use. In the United States, DuPont Corporation was one of the first companies to begin producing polyester fabrics on a large scale, under the brand name Dacron.
Polyester fabrics quickly gained popularity in the 1960s and 1970s due to their durability, ease of care, and low cost. They were widely used in clothing, home furnishings, and industrial applications.
Today, polyester fabrics continue to be popular due to their versatility, durability, and low cost. They are often blended with other fibers such as cotton, wool, or silk to create fabrics with unique properties and characteristics. Additionally, the development of recycled polyester has helped reduce the environmental impact of polyester production and use.
Differences in Durability and Strength.
Non-woven fabric and polyester fabric are both commonly used materials in various industries, including textiles, medical, automotive, and construction. While both fabrics share some similarities, such as being synthetic and made from plastic, there are notable differences in their durability and strength.
Durability refers to a material’s ability to withstand wear, tear, and decay over time. In general, non-woven fabric is less durable than polyester fabric. Non-woven fabrics are typically made from a combination of fibers, which are bonded together with heat, pressure, or chemicals. This bonding process can weaken the fibers and make the fabric more prone to tearing or pilling over time. On the other hand, polyester fabric is made from long-chain polymers that are tightly woven together, making it more resistant to wear and tear.
Strength refers to a material’s ability to resist external forces, such as tension or compression. In this regard, polyester fabric is typically stronger than non-woven fabric. The tightly woven structure of polyester fabric gives it a high tensile strength, which means it can withstand a significant amount of force without breaking. Non-woven fabric, however, may be more prone to tearing or stretching under stress.
In summary, while both non-woven fabric and polyester fabric have their own unique properties and applications, polyester fabric is generally more durable and stronger than non-woven fabric. However, non-woven fabric may be more cost-effective and suitable for certain applications, such as disposable medical products or filtration systems.
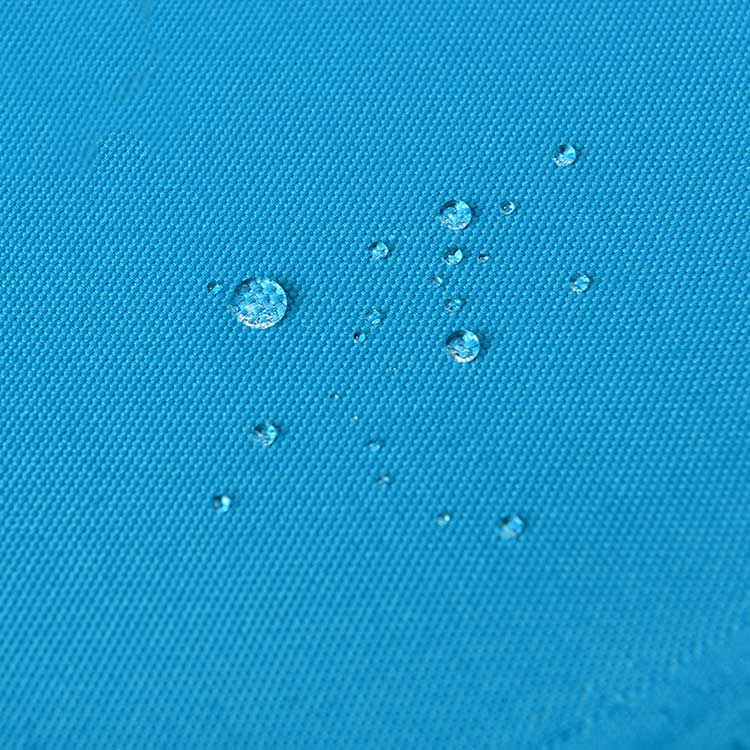

Differences in Water Resistance and Breathability.
Water resistance and breathability are important properties to consider when choosing between non-woven fabric and polyester fabric.
Water resistance refers to a material’s ability to repel or resist the penetration of water. Polyester fabric is generally more water-resistant than non-woven fabric. Polyester fibers have a hydrophobic nature, meaning they naturally repel water. Additionally, polyester fabrics can be treated with water-resistant coatings or finishes, further enhancing their water resistance.
Non-woven fabric, on the other hand, is typically less water-resistant than polyester fabric. This is because non-woven fabric is made from a combination of fibers that are not woven together, but rather bonded together using heat, pressure, or chemicals. This bonding process can create gaps or spaces between the fibers, making the fabric more porous and less water-resistant.
Breathability refers to a material’s ability to allow air and moisture to pass through. In general, non-woven fabric is more breathable than polyester fabric. The bonding process used to create non-woven fabric creates small air pockets between the fibers, allowing air and moisture to pass through more easily. This makes non-woven fabric a popular choice for applications where breathability is important, such as medical textiles or hygiene products.
Polyester fabric, on the other hand, is generally less breathable than non-woven fabric. The tightly woven structure of polyester fabric can make it more difficult for air and moisture to pass through, although some polyester fabrics are treated with moisture-wicking finishes to help improve breathability.
In summary, when it comes to water resistance, polyester fabric is generally more resistant than non-woven fabric. When it comes to breathability, non-woven fabric is generally more breathable than polyester fabric. However, there are many factors that can impact the water resistance and breathability of a specific fabric, such as the type of fibers used, the weaving or bonding process, and any treatments or finishes applied to the fabric.
Cost Comparison and Environmental Impact.
Cost-wise, non-woven fabric is generally less expensive than polyester fabric. This is because non-woven fabric is typically made from a blend of lower-cost fibers and is manufactured using a simpler process that requires less energy and equipment. Additionally, non-woven fabric can be produced in a continuous roll, making it more efficient and cost-effective to produce.
Polyester fabric is generally more expensive than non-woven fabric. This is because it is made from higher-quality synthetic fibers and requires a more complex manufacturing process, which can be energy-intensive and require specialized equipment.
When it comes to environmental impact, both non-woven fabric and polyester fabric have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Non-woven fabric is generally considered to have a lower environmental impact than polyester fabric, as it is often made from recycled fibers and can be recycled again after use. Additionally, the simpler manufacturing process used to produce non-woven fabric can result in lower energy consumption and fewer emissions than polyester fabric production.
Polyester fabric is made from non-renewable resources and is not biodegradable, which means it can contribute to landfill waste if not properly disposed of. However, some polyester fabrics are made from recycled materials, which can help to reduce their environmental impact. Additionally, polyester fabric is generally more durable than non-woven fabric, which means it may need to be replaced less frequently, reducing the overall environmental impact over time.
In summary, when it comes to cost, non-woven fabric is generally less expensive than polyester fabric. When it comes to environmental impact, non-woven fabric is generally considered to have a lower impact than polyester fabric, but both materials have their own set of advantages and disadvantages that should be considered in the context of the specific application and use case.



